Teradata Vantage Engine Architecture and Concepts
Overview
This article explains the underlying concepts of Teradata Vantage engine architecture. All editions of Vantage, including the Primary Cluster in VantageCloud Lake utilize the same engine.
Teradata's architecture is designed around a Massively Parallel Processing (MPP), shared-nothing architecture, which enables high-performance data processing and analytics. The MPP architecture distributes the workload into multiple vprocs or virtual processors. The virtual processor where query processing takes place is commonly referred to as an Access Module Processor (AMP). Each AMP is isolated from other AMPs, and processes the queries in parallel allowing Teradata to process large volumes of data rapidly.
The major architectural components of the Teradata Vantage engine include the Parsing Engines (PEs), BYNET, Access Module Processors (AMPs), and Virtual Disks (Vdisks). Vdisks are assigned to AMPs in enterprise platforms, and to the Primary Cluster in the case of VantageCloud Lake environments.
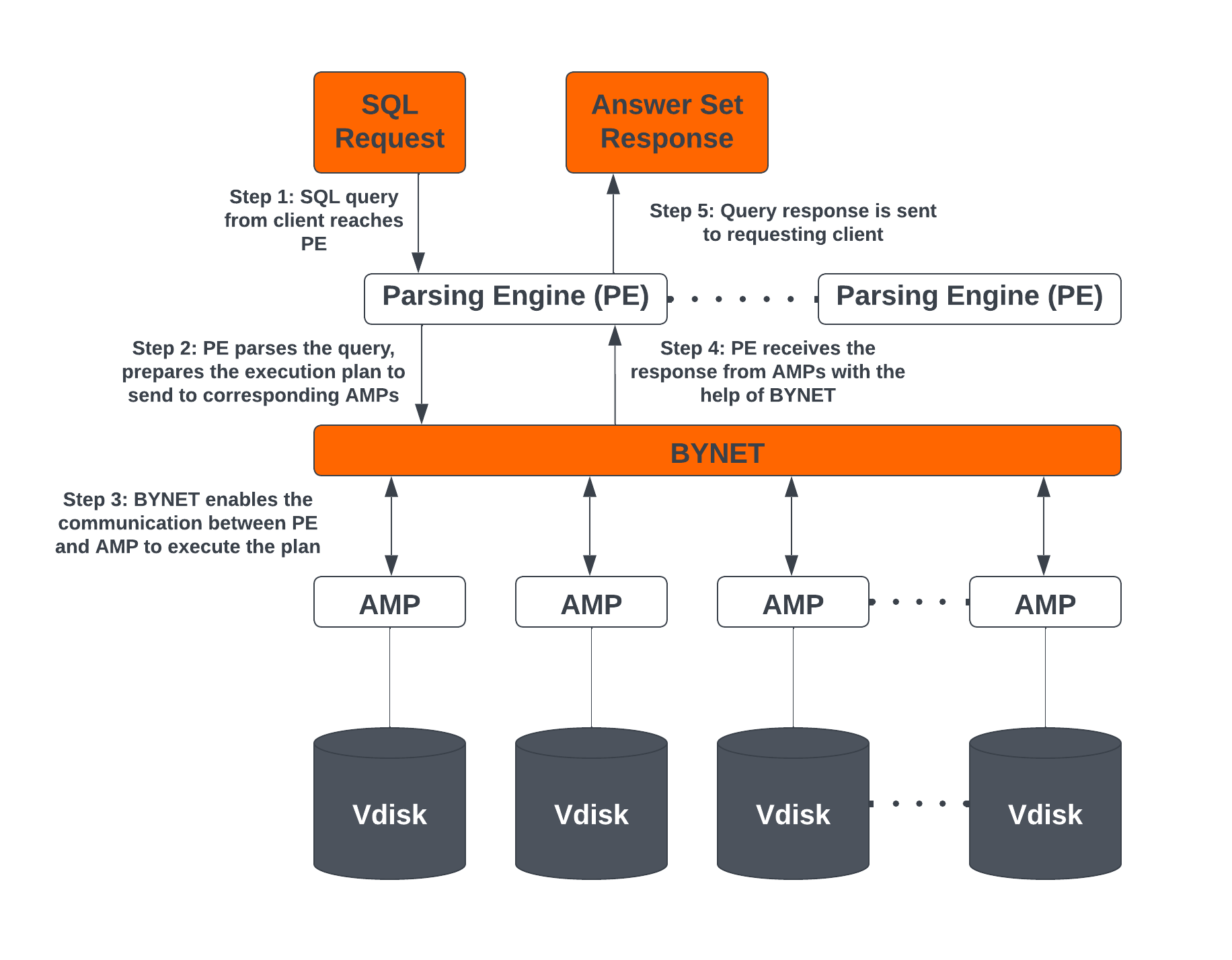
Teradata Vantage Engine Architecture Components
The Teradata Vantage engine consists of the components below:
Parsing Engines (PE)
When a SQL query is run in Teradata, it first reaches the Parsing Engine. The functions of the Parsing Engine are:
- Manage individual user sessions (up to 120).
- Check if the objects used in the SQL query exist.
- Check if the user has required privileges against the objects used in the SQL query.
- Parse and optimize the SQL queries.
- Prepare the execution plan to execute the SQL query and passes it to the corresponding AMPs.
- Receive the response from the AMPs and send it back to the requesting client.
BYNET
BYNET is a system that enables component communication. The BYNET system provides high-speed bi-directional broadcast, multicast, and point-to-point communication and merge functions. It performs three key functions: coordinating multi-AMP queries, reading data from multiple AMPs, regulating message flow to prevent congestion, and processing platform throughput. These functions of BYNET make Vantage highly scalable and enable Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) capabilities.
Parallel Database Extension (PDE)
Parallel Database Extension (PDE) is an intermediary software layer positioned between the operating system and the Teradata Vantage database. PDE enables MPP systems to use features such as BYNET and shared disks. It facilitates the parallelism that is responsible for the speed and linear scalability of the Teradata Vantage database.
Access Module Processor (AMP)
AMPs are responsible for data storage and retrieval. Each AMP is associated with its own set of Virtual Disks (Vdisks) where the data is stored, and no other AMP can access that content in line with the shared-nothing architecture. The functions of AMP are:
- Access storage using Vantage’s Block File System Software
- Lock management
- Sorting rows
- Aggregating columns
- Join processing
- Output conversion
- Disk space management
- Accounting
- Recovery processing
AMPs in VantageCore IntelliFlex, VantageCore VMware, VantageCloud Enterprise, and the Primary Cluster in the case of VantageCloud Lake, store data in a Block File System (BFS) format on Vdisks. AMPs in Compute Clusters and Compute Worker Nodes on VantageCloud Lake do not have BFS, they can only access data in object storage using the Object File System (OFS).
Virtual Disks (Vdisks)
These are units of storage space owned by an AMP. Virtual Disks are used to hold user data (rows within tables). Virtual Disks map to physical space on a disk.
Node
A node, in the context of Teradata systems, represents an individual server that functions as a hardware platform for the database software. It serves as a processing unit where database operations are executed under the control of a single operating system. When Teradata is deployed in a cloud, it follows the same MPP, shared-nothing architecture but the physical nodes are replaced with virtual machines (VMs).
Teradata Vantage Architecture Concepts
The concepts below are applicable to Teradata Vantage.
Linear Growth and Expandability
Teradata is a linearly expandable RDBMS. As the workload and data volume increase, adding more hardware resources such as servers or nodes results in a proportional increase in performance and capacity. Linear Scalability allows for increased workload without decreased throughput.
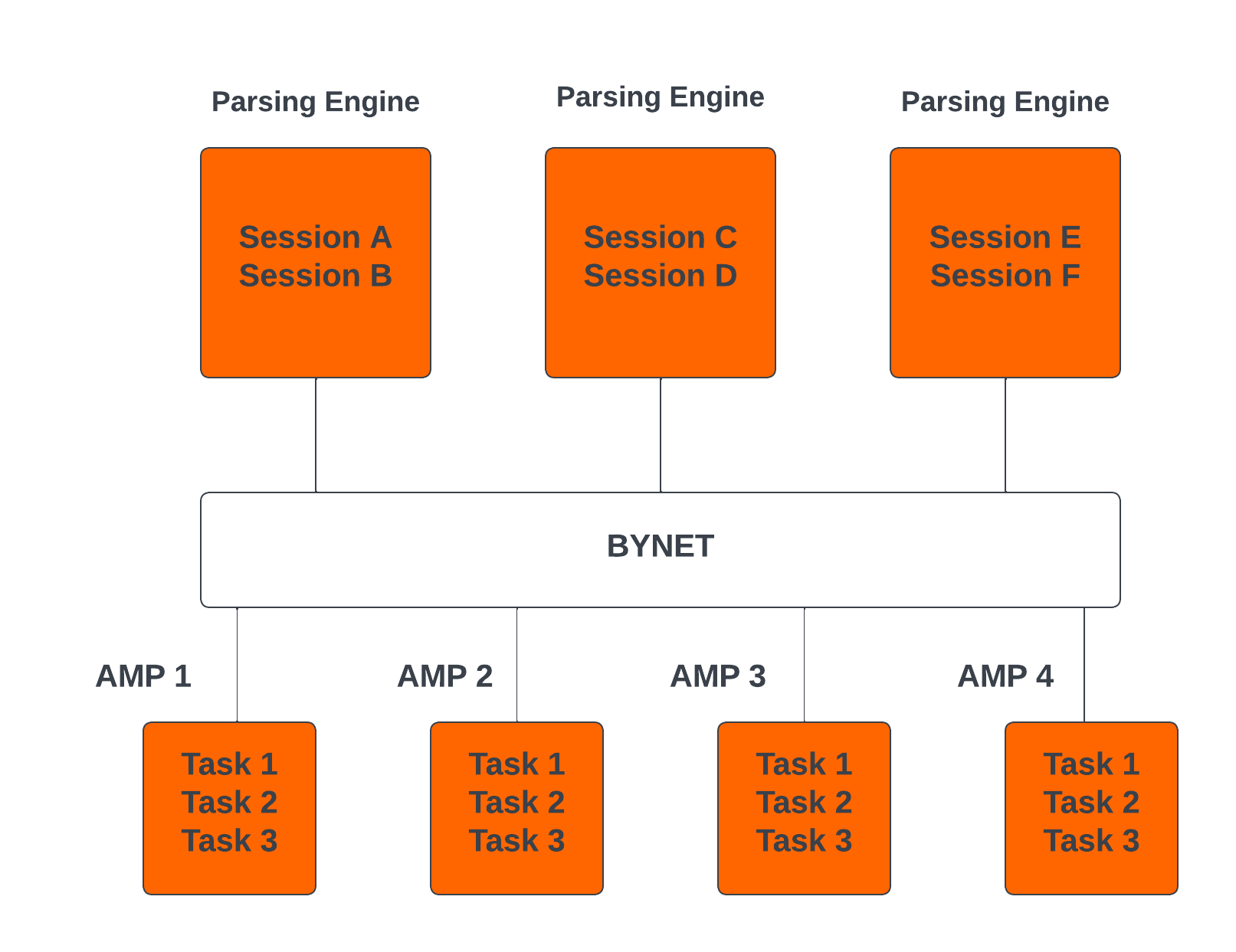
Teradata Parallelism
Teradata parallelism refers to the inherent ability of the Teradata Database to perform parallel processing of data and queries across multiple nodes or components simultaneously.
- Each Parsing Engine (PE) in Teradata has the capability to handle up to 120 sessions concurrently.
- The BYNET in Teradata enables parallel handling of all message activity, including data redistribution for subsequent tasks.
- All Access Module Processors (AMPs) in Teradata can collaborate in parallel to serve any incoming request.
- Each AMP can work on multiple requests concurrently, allowing for efficient parallel processing.
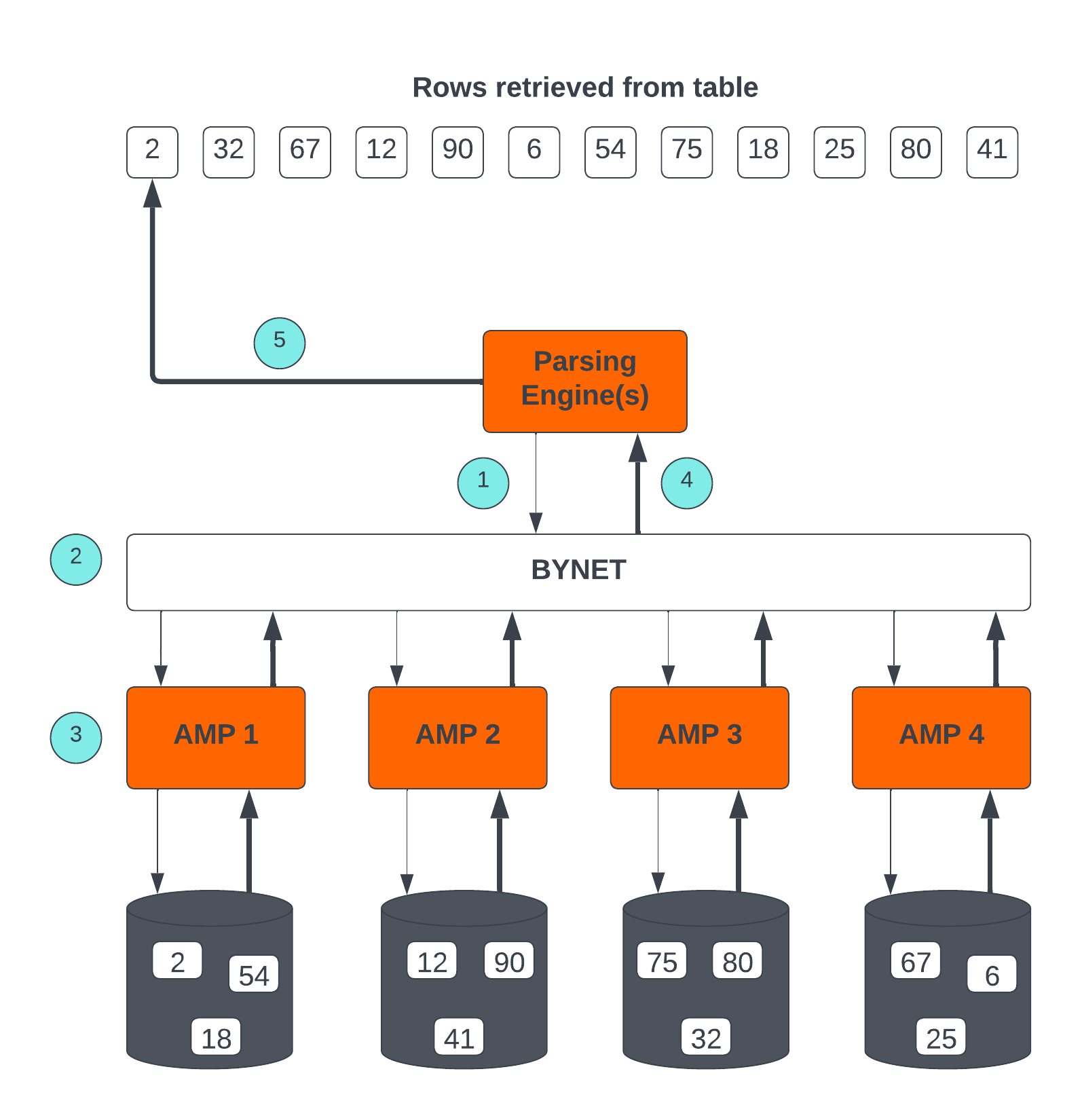
Teradata Retrieval Architecture
The key steps involved in Teradata Retrieval Architecture are:
- The Parsing Engine sends a request to retrieve one or more rows.
- The BYNET activates the relevant AMP(s) for processing.
- The AMP(s) concurrently locate and retrieve the desired row(s) through parallel access.
- The BYNET returns the retrieved row(s) to the Parsing Engine.
- The Parsing Engine then delivers the row(s) back to the requesting client application.
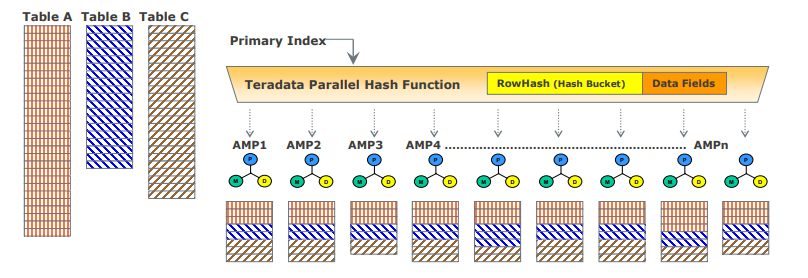
Teradata Data Distribution
Teradata's MPP architecture requires an efficient means of distributing and retrieving data and does so using hash partitioning. Most tables in Vantage use hashing to distribute data for the tables based on the value of the row’s Primary Index (PI) to disk storage in Block File System (BFS) and may scan the entire table or use indexes to access the data. This approach ensures scalable performance and efficient data access.
- If the Primary Index is unique then the rows in the tables are automatically distributed evenly by hash partitioning.
- The designated Primary Index column(s) are hashed to generate consistent hash codes for the same values.
- No reorganization, repartitioning, or space management is required.
- Each AMP typically contains rows from all tables, ensuring efficient data access and processing.
Conclusion
In this article, we covered the major architectural components of Teradata Vantage, such as the Parsing Engines (PEs), BYNET, Access Module Processors (AMPs), Virtual Disk (Vdisk), other architectural components such as Parallel Database Extension (PDE), Node and the essential concepts of Teradata Vantage such as Linear Growth and Expandability, Parallelism, Data Retrieval, and Data Distribution.