Run Teradata Jupyter Notebook Demos for VantageCloud Lake in Visual Studio Code
Overview
Visual Studio Code is a popular open-source code editor compatible with Windows, MacOs, and Linux. Developers use this Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for coding, debugging, building, and deploying applications. In this quickstart guide, we launch VantageCloud Lake Jupyter notebook demos within Visual Studio Code.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following prerequisites in place:
- Docker Desktop installed
- Git installed
- Required to download git repo from https://github.com/Teradata/lake-demos.git
- Visual Studio Code installed
- A Teradata VantageCloud Lake account with organization URL and login details from the Teradata welcome letter
- Once logged in follow these instructions to create a VantageCloud Lake Enviorment
Clone VantageCloud Lake Demo repository
Begin by cloning the GitHub repository and navigating to the project directory:
Start a Jupyterlab docker container with Teradata Jupyter Exensions
To launch Teradata VantageCloud Lake demos, we need the Teradata Jupyter Extensions for Docker. These extensions provide the SQL ipython kernel, utilities to manage connections to Teradata, and the database object explorer to make you productive while interacting with the Teradata database.
Next, start a container and bind it to the existing lake-demos directory. Choose the appropriate command based on your operating system:
For Windows, run the docker command in PowerShell.
- Windows
- MacOS
- Linux
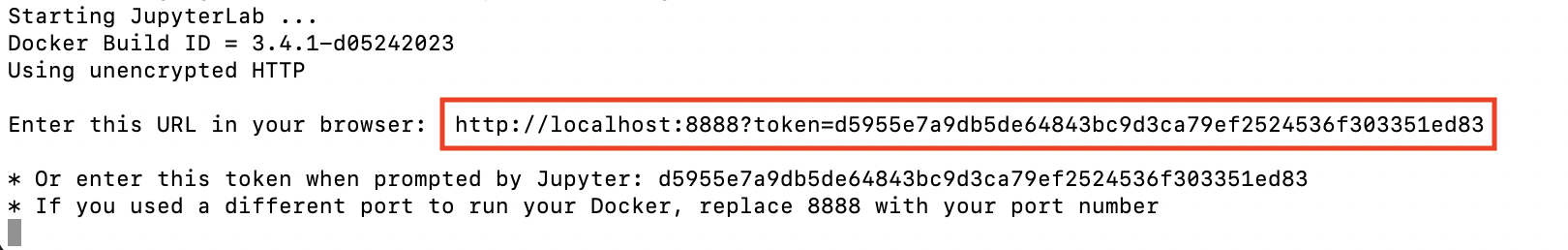
Take note of the resulting URL and token; you’ll need them to establish the connection from Visual Studio Code.
Visual Studio Code Configuration
Open lake-demos project directory in Visual Studio Code. The repository contains the following project tree:
LAKE_DEMOS
Edit vars.json file
Edit the vars.json file to include the required credentials to run the demos
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| "host" | Public IP value from your VantageCloud Lake environment |
| "UES_URI" | Open Analytics from your VantageCloud Lake environment |
| "dbc" | The master password of your VantageCloud Lake environment. |
To retrieve a Public IP address and Open Analytics Endpoint follow these instructions
Change passwords in the vars.json file. You'll see that in the sample vars.json, the passwords of all users are defaulted to "password", this is just for matters of the sample file, you should change all of these password fields to strong passwords, secure them as necessary and follow other password management best practices.
Modify path to vars.json in UseCases directory
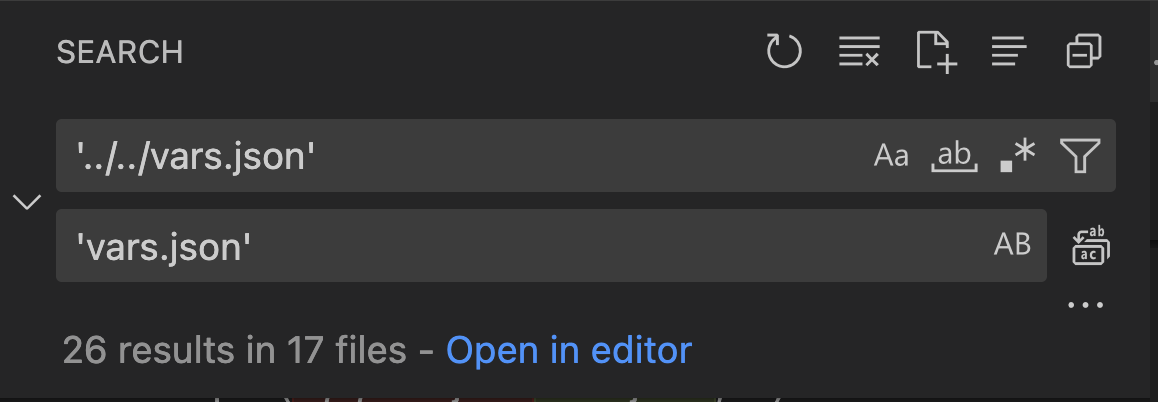
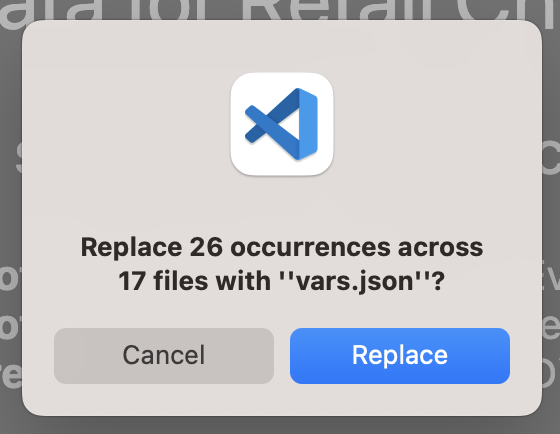
In the UseCases directory, all .ipynb files use the path ../../vars.json to load the variables from the JSON file when working from Jupyterlab. To work directly from Visual Studio Code, update the code in each .ipynb to point to vars.json.
The quickest way to make these changes is via search feature on the left vertical menu. Search for
and replace with:
Configuring Jupyter Kernels
Open 0_Demo_Environment_Setup.ipynb and click on Select Kernel at the top right corner of Visual Studio Code.
If you have not installed Jupyter and Python extensions, Visual Studio Code will prompt you to install them. These extensions are necessary for Visual Studio Code to detect Kernels. To install them, select 'Install/Enable suggested extensions for Python and Jupyter.'
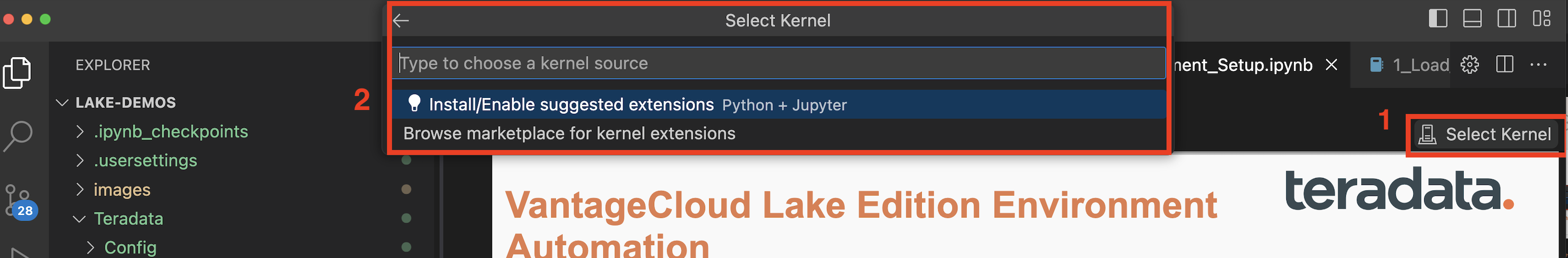
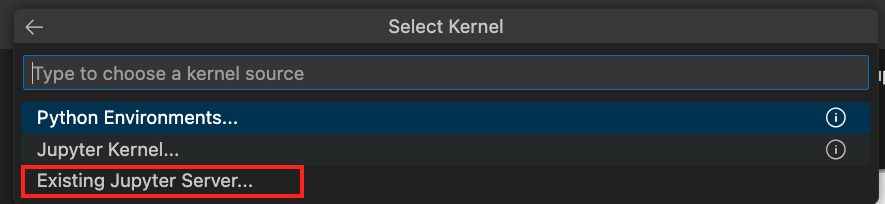
Once you've installed the necessary extensions, you'll find options in the drop-down menu. Choose Existing Jupyter Kernel.
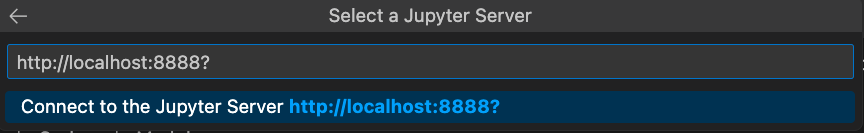
Enter the URL of the running Jupyter Server and press enter.
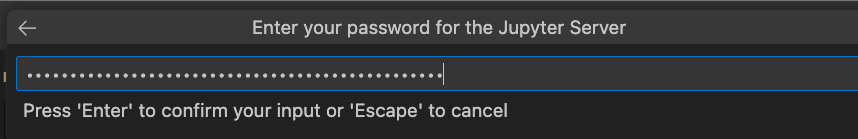
Enter the token found in your terminal when mounting files to the Docker container and press Enter.
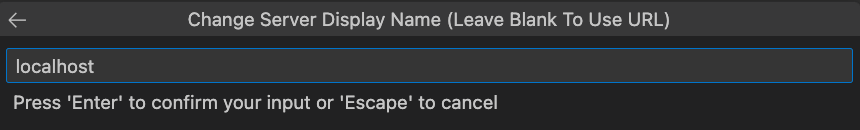
Change Server Display Name (Leave Blank To Use URL)
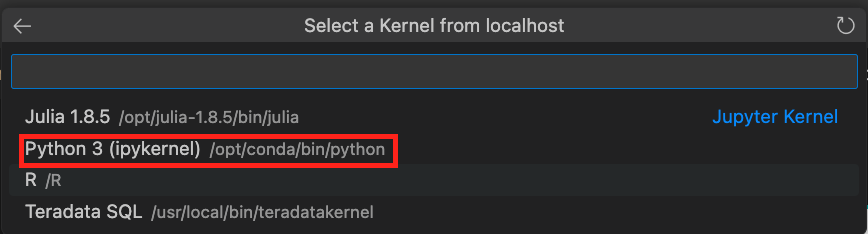
You now have access to all the Teradata Vantage extension kernels. Select Python 3 (ipykernel) from the running Jupyter server.
Run demos
Execute all the cells in 0_Demo_Environment_Setup.ipynb to setup your environment. Followed by 1_Demo_Setup_Base_Data.ipynb to load the base data required for demo. To learn more about the demo notebooks, go to Teradata Lake demos page on GitHub.
Summary
In this quickstart guide, we configured Visual Studio Code to access VantageCloud Lake demos using Jupyter notebooks.